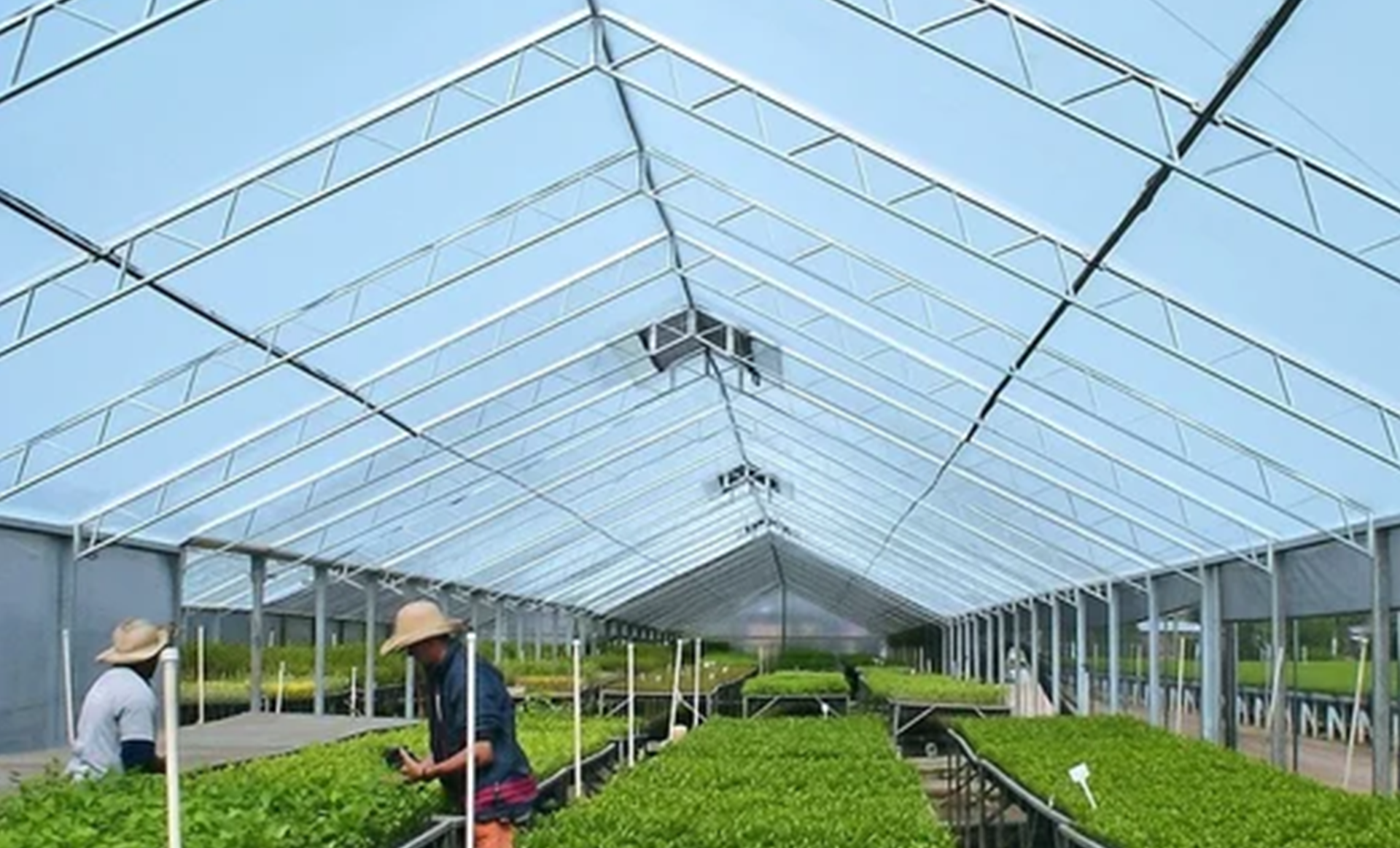
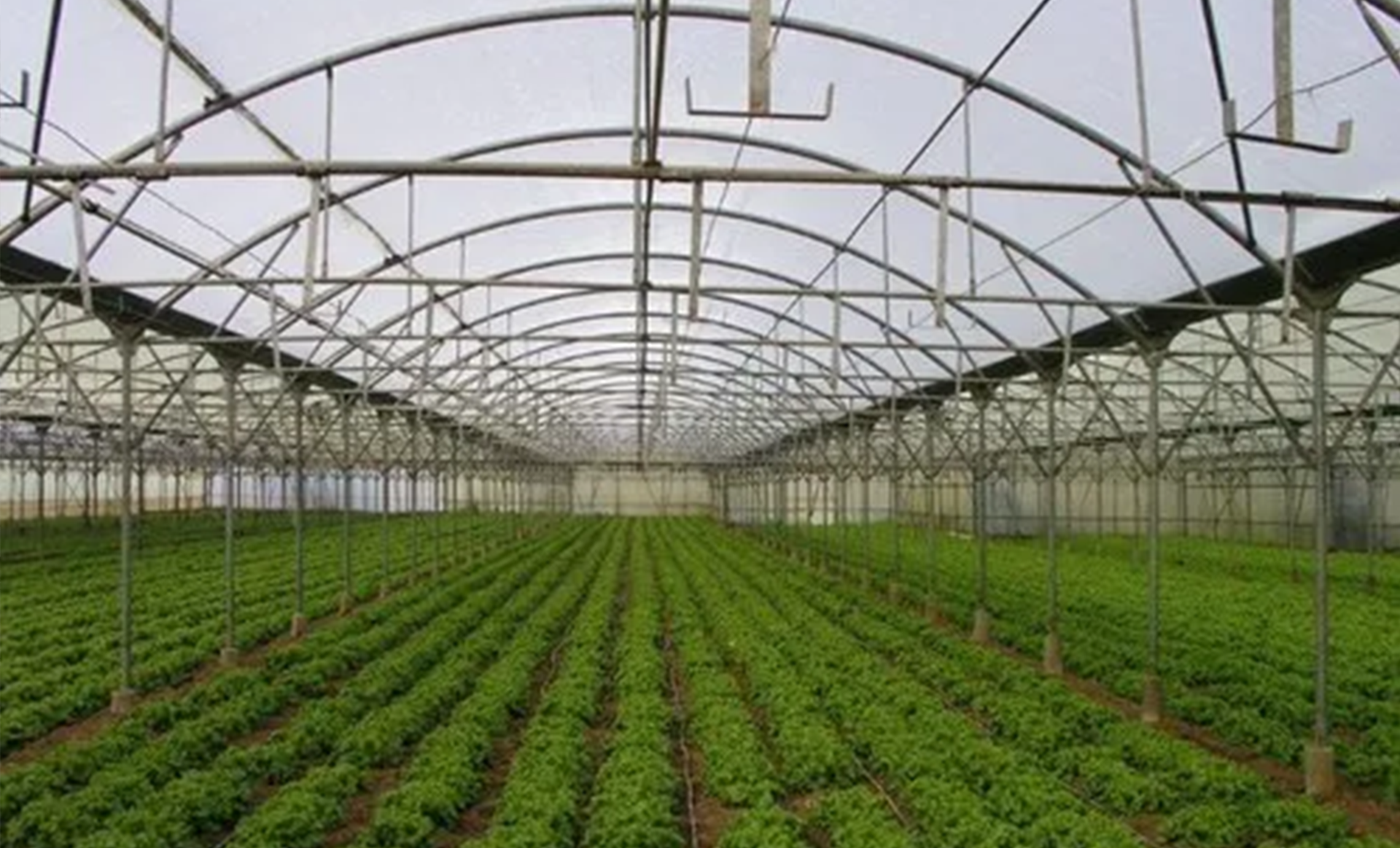
Agriculture /Green House industry
The greenhouse industry generates internal residues, as other agricultural activities, that affect soil and water and external wastes, such as plastics and plant biomass debris. Almost all of the plastic waste from the greenhouses is recycled.
View moreabout our services
Agriculture /Green House industry
Applications
Year-round Crop Production
Greenhouses allow farmers to grow crops year-round, regardless of
Greenhouses allow farmers to grow crops year-round, regardless of seasonal or climatic limitations. This ensures a consistent and reliable food supply, reduces dependence on seasonal fluctuations, and increases market competitiveness.
Urban Agriculture
Greenhouses are increasingly used in urban and peri-urban areas for local
Greenhouses are increasingly used in urban and peri-urban areas for local food production. Urban farms and rooftop gardens utilize vertical farming techniques and compact greenhouse structures to maximize space and meet the growing demand for fresh produce in cities.
Research and Education
Greenhouses serve as valuable research and educational tools for
Greenhouses serve as valuable research and educational tools for studying plant physiology, agronomy, and horticulture. Academic institutions, research organizations, and agricultural extension services use greenhouse facilities to conduct experiments, demonstrations, and training programs.
Specialty Crop Production
Greenhouses enable the production of high-value specialty crops
Automotive manufacturers implement rigorous quality control processes to ensure that vehicles meet safety, performance, and reliability standards. Quality control measures include inspection of components, assembly line testing, and vehicle validation testing under various operating conditions.
Climate Change Adaptation
Greenhouses play a role in climate change adaptation by providing
Greenhouses play a role in climate change adaptation by providing a buffer against extreme weather events, temperature fluctuations, and changing growing conditions. Climate-resilient greenhouse designs and technologies help mitigate risks and ensure food security in a changing climate.
Climate Control Systems
Greenhouses are equipped with climate control systems that regulate temperature, humidity, and ventilation to create optimal growing conditions for plants.
Nutrient Management Systems
Nutrient management systems deliver essential nutrients to plants through fertigation (fertilization through irrigation water) or hydroponic solutions.
Energy Efficiency Features
Greenhouses incorporate energy-efficient design features such as insulated glazing, thermal curtains, and energy-efficient heating and cooling
Environmental Monitoring Sensors
Greenhouses are equipped with environmental monitoring sensors that measure parameters such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and CO2 levels.
Role of greenhouse in agriculture
This technology of using greenhouses to grow plants is of significant importance, especially in areas where the climatic conditions are always on the extreme side and regions of high rainfall. Also, greenhouses are wonderful as utilizing space for growing plants has never been this efficient