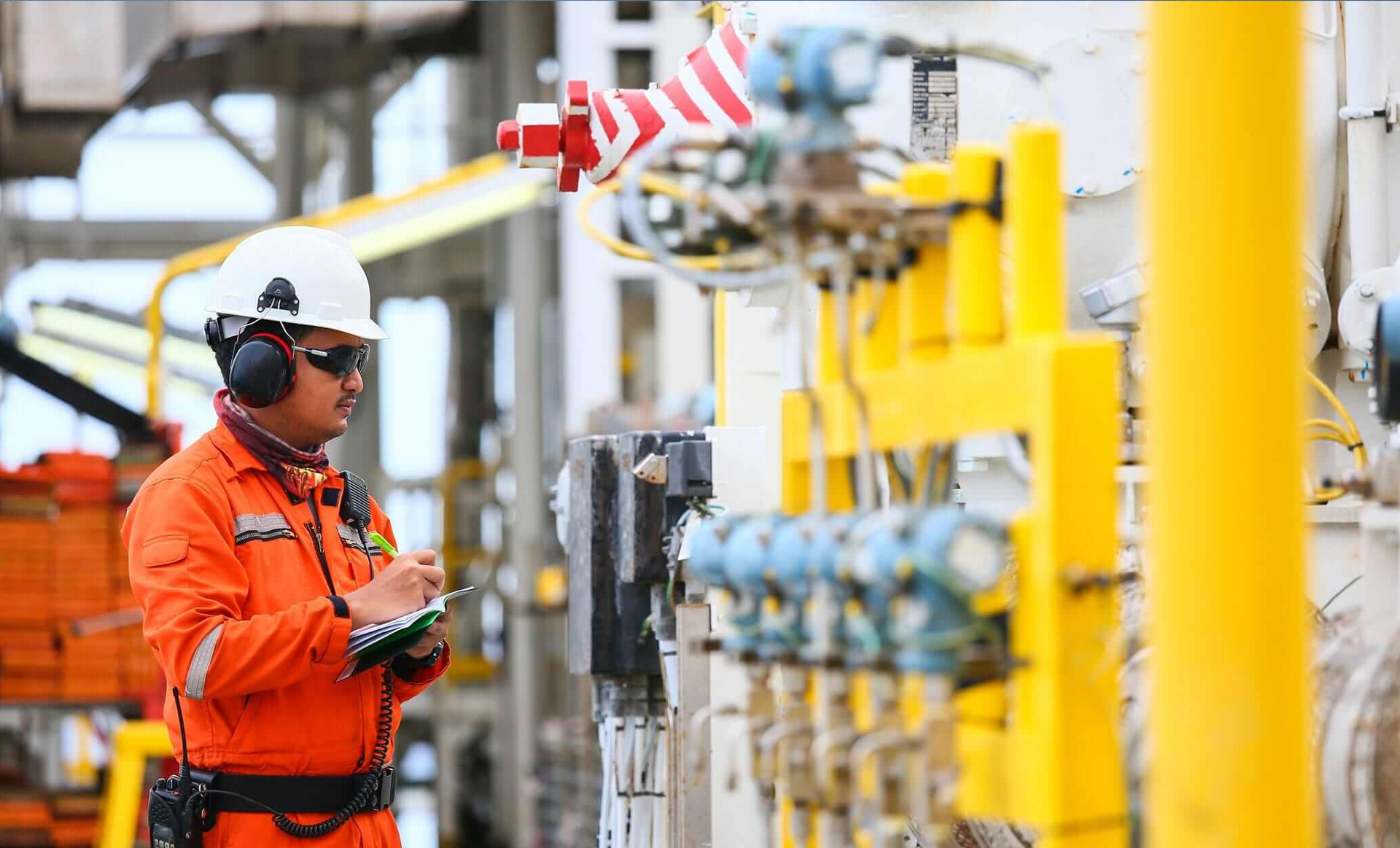
Oil & Gas
With an anticipated $5 trillion in worldwide revenue as of 2022, the oil and gas business is one of the largest in terms of dollar value in the globe. Oil has a significant impact on all aspects of the global economic system, including transportation, heating, energy, industrial output, and manufacturing.
View moreabout our services
Oil and Gas
Applications
Exploration and Production
Seismic surveys: Using seismic waves to map subsurface geology
Seismic surveys: Using seismic waves to map subsurface geology and identify potential reservoirs. Drilling: Extracting oil and gas from underground reservoirs through drilling operations, including conventional drilling and hydraulic fracturing (fracking).
Transportation
Pipelines: Transporting crude oil, natural gas, and refined products
Pipelines: Transporting crude oil, natural gas, and refined products over long distances via pipeline networks. Tankers: Shipping crude oil and liquefied natural gas (LNG) across oceans using specialized tankers.
Refining and Processing
Refineries: Processing crude oil into various refined products such as gasoline
Refineries: Processing crude oil into various refined products such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and petrochemical feedstocks. Petrochemical plants: Converting natural gas and crude oil derivatives into chemicals used in plastics, pharmaceuticals, fertilizers, and other products.
Power Generation
Natural gas power plants: Generating electricity by burning natural gas
Natural gas power plants: Generating electricity by burning natural gas to power turbines and generators. Combined heat and power (CHP) plants: Using natural gas to generate both electricity and heat for industrial and commercial facilities.
Heating and Cooling
Residential and commercial heating: Using natural gas for space heating and water
Residential and commercial heating: Using natural gas for space heating and water heating in homes, offices, and buildings. Industrial heating: Providing process heat for industrial applications such as refining, manufacturing, and food processing.
Energy Transition
The industry is undergoing a transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources in response to climate change concerns and evolving consumer preferences.
Regulatory Compliance
The industry is subject to extensive regulation at local, national, and international levels to ensure safety, environmental protection, and resource management.
Geopolitical Influence
The resources are often located in geopolitically sensitive regions, leading to geopolitical tensions, conflicts, and strategic alliances among nations.
Cyclical Nature
The industry is cyclical, characterized by periods of boom and bust driven by factors such as commodity prices, supply-demand dynamics, economic conditions.
Oil & Gas Industry Outlook
The industry has finally recovered in light of recent low points, including the price collapse in 2013 and significant environmental catastrophes, such the Deepwater Horizon Gulf of Mexico Oil Spill in 2014. As the world’s industries and infrastructure continue to rely significantly on petroleum-based products, the world’s dependence on oil and gas is growing.