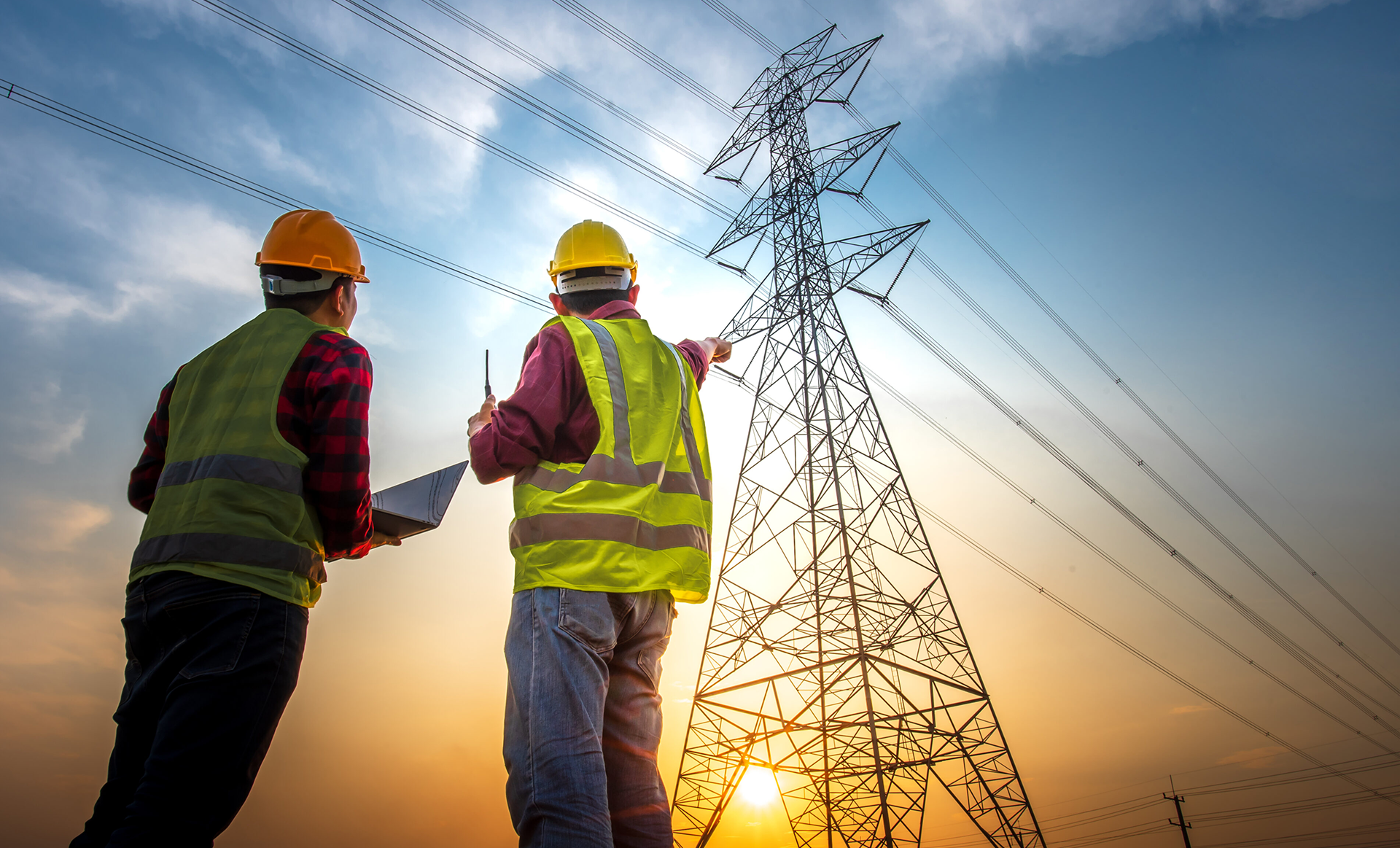
Power Transmission
Electric power transmission as a field did not exist until the late 19th century. Direct current (DC) was used in the earliest electric generating since it could not be easily increased in voltage for long-distance transmission.
View moreabout our services
Power Transmission & Energy
Applications
Renewable Energy Integration
With the increasing focus on sustainability, there's a growing
With the increasing focus on sustainability, there's a growing emphasis on integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. This requires technologies for managing intermittent power generation from sources like solar and wind.
Energy Storage
Energy storage systems, such as batteries, pumped hydro storage
Energy storage systems, such as batteries, pumped hydro storage, and flywheels, play a crucial role in balancing supply and demand on the grid and storing excess energy generated during off-peak hours for use during peak times.
Distributed Generation
This refers to small-scale power generation located close to the
This refers to small-scale power generation located close to the point of use, such as rooftop solar panels or small wind turbines. Distributed generation can improve grid resilience and reduce transmission losses.
Grid Modernization
Aging infrastructure and the need for increased reliability
Aging infrastructure and the need for increased reliability and efficiency drive efforts to modernize power grids through investments in new technologies, automation, and improved grid management systems.
Electric Vehicles
The rise of electric vehicles presents both challenges
The rise of electric vehicles presents both challenges and opportunities for the energy sector. EV charging infrastructure and grid integration technologies are important areas of focus for enabling widespread adoption of electric transportation.
Efficiency
Efficiency is paramount in power transmission and energy systems to minimize losses during generation, transmission, and distribution.
Reliability
Redundancy, proper maintenance, and robust design of equipment and infrastructure contribute to system reliability.
Flexibility
Flexibility allows the power system to adapt to fluctuations in supply and demand, particularly important with the increasing penetration of renewable energy sources
Scalability
Power transmission and energy systems must be scalable to accommodate changing demand patterns, integration of renewable energy sources.
Energy Transmission
Transmission of energy is used to deal with the temporal mismatch between the production of (renewable) energy and changes in demand, in addition to transferring energy from the primary sites of generation to those sites. As a result, energy storage and transmission may be complementary.